Why PCB controls 50 ohm impedance
single-ended network in the design is generally controlled by 50 ohms, so many people will ask, why is it required to be controlled by 50 ohms instead of 25 ohms or 80 ohms? First of all, 50 ohms is selected by default, and everyone in the industry accepts this value. Generally speaking, it must be a standard set by a recognized organization, and everyone designs according to the standard.
Using the reference clock to realize serial communication data recovery of Cyclone10LP devices
In the non-source synchronous low-speed serial data communication scenario, the clock frequency of the communication counterpart may be biased, which may cause the data receiving end to be unable to accurately sample. In this case, the SOFT-CDR and DPA functions in the high-speed transceiver or LVDS serdes of high-end Altera devices can effectively solve this problem.
CR2032 vs CR2450 batteries: Which one is better for your device?
Many daily devices use CR2032 and CR2450 batteries because of their small size and reliable performance.
7408 Integrated Circuit: A Classic TTL (transistor-transistor logic) Type IC
The 7408 integrated circuit is a classic TTL (transistor-transistor logic) type IC, which is widely used in various digital circuits. It contains four 2-input AND gates, each with two inputs and one output, for performing logical AND operations.
What is Transistor hFE
hFE, also known as current gain or β (Beta), is an important parameter of the transistor, which represents the ratio between the base current and the collector current. It describes the gain capability of a transistor when amplifying current.
IGBT vs. MOSFET: A Comprehensive Comparison of Features
Both IGBTs and MOSFETs are important semiconductor devices that are widely used in power electronics, switching power supplies, and other high-power control systems. They can both be used to control the flow of current, but their operating principles, characteristics, and application scenarios differ.
WiFi 7 vs WiFi 6: Wireless Network Routing Comparison
WiFi 7 (802.11be) and WiFi 6 (802.11ax) are both wireless network communications standards, but they have significant differences in performance, spectral efficiency, latency, and the number of devices they support.
ENIG vs ENEPIG PCB: Explore the Difference
The choice of PCB surface finish is more than just a detail; it determines the performance and lifespan of the PCB. The versatile and robust Electroless Nickel Electroless Palladium Immersion Gold (ENEPIG) and the reliable and classic Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG).
The automotive crystal oscillator FA-238A is the preferred choice for car Bluetooth
Epson FA-238A is a high-performance quartz crystal oscillator widely used in automotive, industrial and consumer electronics fields. It is particularly suitable for automotive-grade and high-reliability applications, with excellent temperature stability, low power consumption and high precision.
What are the differences between tantalum capacitors and ordinary capacitors
Tantalum capacitors are often used in high-precision circuits due to their high reliability, stability and small size, but due to their high price and polarity requirements, special attention should be paid to the connection polarity during design.
What is a clamping diode? Principle, function and application analysis
Clamping diodes are a common electronic component, also known as protection diodes or baropendulum diodes.
Four Common Topological Approaches to Powering LEDs
There are many topologies that can be used to power LEDs. As you probably already know, you need to first identify your design requirements before you start selecting, or you may end up with a design that is less than ideal or, worse, not guaranteed to work properly over the long term.
Regionalization Trend of Global Electronic Component Manufacturing: The Impact of Multinational Joint Ventures and Supply Chain Diversification
As global supply chain pressure increases, more and more electronic component companies are establishing production bases in places such as India and Southeast Asia, promoting the regionalization of supply chains.
US CHIPS Act 2024 in-depth implementation: How to reshape the global semiconductor supply chain and the future of technology
In August 2024, as the CHIPS Act is further promoted, the United States strives to localize the semiconductor industry and reduce external dependence. This strategic transformation is reshaping the global chip supply chain and is crucial to the future development of emerging technology fields such as AI and big data. This article deeply analyzes how the CHIPS Act reshapes the global supply chain and brings key industry impacts.
Hisense TVs sold out in Walmart on Black Friday
During this year's Black Friday promotion, Hisense TVs once again became a hot-selling product in the United States. Recently, a large number of videos of Americans rushing to buy Hisense TVs appeared on social media.
WiFi 7 vs WiFi 6: Wireless Network Routing Comparison

WiFi 7 (802.11be) and WiFi 6 (802.11ax) are both wireless network communications standards, but they have significant differences in performance, spectral efficiency, latency, and the number of devices they support. WiFi 7 is the successor to WiFi 6 and is designed to deliver higher speeds, lower latency, and greater multi-device support.
WiFi 7 VS WiFi 6 :A Comparative Analysis
| Feature | WiFi 6 (802.11ax) | WiFi 7 (802.11be) |
|---|---|---|
| Max Theoretical Speed | 9.6 Gbps (with 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bandwidth) | 46 Gbps (with 6 GHz bandwidth, maximum theoretical) |
| Spectrum Support | 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz | 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz |
| Max Channel Bandwidth | 160 MHz | 320 MHz |
| Speed per Stream | Up to 1.2 Gbps (per MIMO stream) | Up to 4.8 Gbps (per MIMO stream) |
| Maximum Number of Users | 8 devices (MU-MIMO and OFDMA) | 16 devices (improved MU-MIMO and OFDMA) |
| Latency | Low | Even lower (as low as 1ms) |
| Multi-Link Operation (MLO) | Not supported | Supported, allowing multiple frequency bands for data transmission |
| OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) | Supported, enabling multiple devices to share bandwidth | Enhanced OFDMA, supports more devices and improves spectrum efficiency |
| Use Cases | Home, office environments, gaming, video streaming | High bandwidth applications, real-time interaction, VR/AR, high-density environments |
| Data Transmission Rate Improvement | 40% improvement over WiFi 5 | Up to 4x improvement over WiFi 6 (maximum theoretical speed) |
| Dynamic Frequency Access (DFA) | Limited (DFS and radar avoidance) | Improved spectrum management, supports more efficient dynamic frequency access |
| Compatibility | Backward compatible with WiFi 5, WiFi 4, and older devices | Backward compatible with WiFi 6 and earlier standards, optimized for new devices |
1. Speed and Throughput
WiFi 7 offers significantly higher speeds, especially in the 6 GHz band. WiFi 7 can reach a maximum throughput of 46 Gbps, while WiFi 6 has a maximum throughput of 9.6 Gbps. This makes WiFi 7 more suitable for high-bandwidth applications such as 8K video streaming, VR/AR, and data-intensive workloads.
2. Spectrum and bandwidth
WiFi 6 supports a channel bandwidth of 160 MHz and operates on the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. WiFi 7 introduces 320 MHz channel bandwidth and supports the 6 GHz band, providing more spectrum, significantly reducing interference, and increasing overall network throughput and speed.
3. Multi-user performance (MU-MIMO)
WiFi 6 introduces OFDMA and MU-MIMO technologies, allowing multiple devices to share bandwidth at the same time, improving network efficiency and throughput. WiFi 7 further enhances these technologies and supports more devices to connect at the same time. It performs better especially in busy network environments and can support 16 users, greatly improving performance in multi-device environments.
4. Delay
WiFi 7 introduces lower latency, especially in supporting low-latency applications (such as games, real-time video conferencing), with latency below 1 millisecond. WiFi 6 already had lower latency by comparison, but WiFi 7 further optimizes responsiveness for high-demand applications.
5. Real-time traffic and Dynamic Spectrum Access (DFA)
WiFi 7 has greatly improved dynamic spectrum access (DFA), supporting more efficient spectrum management to ensure that high-demand applications (such as VR/AR) can obtain priority bandwidth, further reducing interference and lowering latency.
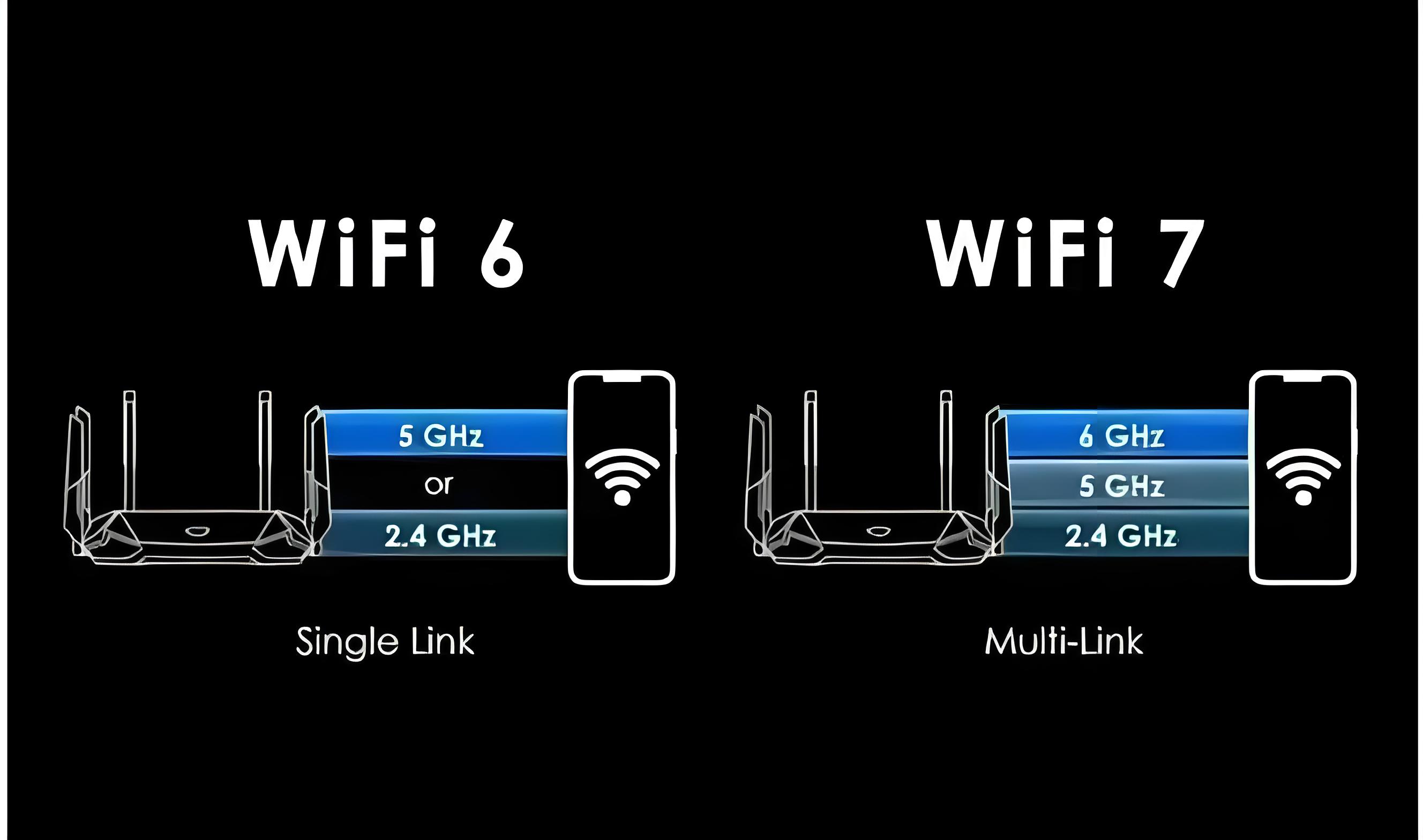
6. Multi-link operation (MLO)
WiFi 7 introduces Multi-Link Operation (MLO), which allows devices to transmit data on multiple frequency bands (such as 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz) simultaneously. This improves reliability, throughput and flexibility, especially when network load is high.
7. Compatibility and Supported Devices
WiFi 6 is already capable of supporting older devices like WiFi 5 and WiFi 4, and most modern devices support WiFi 6. However, WiFi 7 is primarily designed for newer generations of devices and offers backwards compatibility.
WiFi 7 VS. WiFi 6 data rate comparison
WiFi 7 advances in network security and data transmission
WiFi 7 provides significant improvements in network security and data transmission compared to WiFi 6, especially in high-bandwidth applications, real-time low-latency transmission and enhanced security. WiFi 7 supports a more powerful encryption mechanism, enhances the security of open networks, and improves data transmission efficiency through multi-link operation and wider spectrum bandwidth, making it suitable for high-bandwidth, low-latency, and complex environments with multiple devices.
| Feature | WiFi 6 (802.11ax) | WiFi 7 (802.11be) |
|---|---|---|
| Security Protocol | WPA3 | WPA3 Enhanced (improved WPA3) |
| Encryption Protection | Enhanced protection mechanisms | Stronger encryption standards, protection against side-channel attacks |
| Spectrum Bandwidth | 160 MHz | 320 MHz |
| Maximum Data Speed | 9.6 Gbps | 46 Gbps |
| Latency | Low | Lower (as low as 1ms) |
| Multi-Link Operation (MLO) | Not supported | Supported |
| Open Network Security (OWE) | Supported | Stronger encryption for open networks |
| Data Transmission Efficiency | Optimized for data transmission | More efficient data transmission, especially in high-bandwidth and low-latency environments |
WiFi 7 Security Advances
WPA3 Enhanced: WiFi 7 improves WPA3 on the basis of WiFi 6, providing more powerful encryption and attack resistance capabilities, especially when dealing with high-bandwidth data transmission, it can prevent man-in-the-middle attacks (MITM), dictionary attacks, etc.
Stronger open network security: WiFi 7 improves the OWE (Opportunistic Wireless Encryption) security protocol to ensure that data transmission can be encrypted even in open networks without authentication, reducing security risks in open network environments.
Resistance to side-channel attacks: WiFi 7 strengthens protection against side-channel attacks and improves data protection capabilities in malicious attack environments.
WiFi 7 data transmission advancements
Higher data transfer rates: WiFi 7 supports a maximum theoretical transfer rate of up to 46 Gbps, compared to WiFi 6’s maximum transfer rate of 9.6 Gbps. This means WiFi 7 can more efficiently handle high-bandwidth applications such as 8K video streaming, real-time VR/AR, etc.
Wider spectrum bandwidth: WiFi 7 supports up to 320 MHz spectrum bandwidth, double the 160 MHz bandwidth supported by WiFi 6. This enables WiFi 7 to support more data streams transmitting simultaneously, improving overall network efficiency.
Multi-Link Operation (MLO): WiFi 7 introduces MLO, which allows devices to transmit data simultaneously on multiple frequency bands (such as 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz), which greatly increases the reliability, throughput and flexibility of data transmission sex.
Low-latency optimization: WiFi 7 has significantly lower latency, supporting latency as low as 1 millisecond, making it ideal for applications that require real-time data processing, such as high-end gaming, video conferencing, and virtual reality.
More efficient multi-device support: WiFi 7’s OFDMA and MU-MIMO technologies have been further optimized based on WiFi 6, which can support more devices at the same time and improve data transmission efficiency, especially in high-density environments, WiFi 7 can provide More stable performance.
WiFi 7 offers significant improvements in performance and network security over WiFi 6, especially in terms of speed, latency, bandwidth, and multi-device support. WiFi 7 is suitable for scenarios that require extremely high performance and low latency, such as 4K/8K video streaming, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and high-density environments. And WiFi 6 still provides excellent performance in most home and office environments and is highly cost-effective.
WiFi 7 offers significant advantages in performance and future applications, but compatible devices are required to reach its full potential.